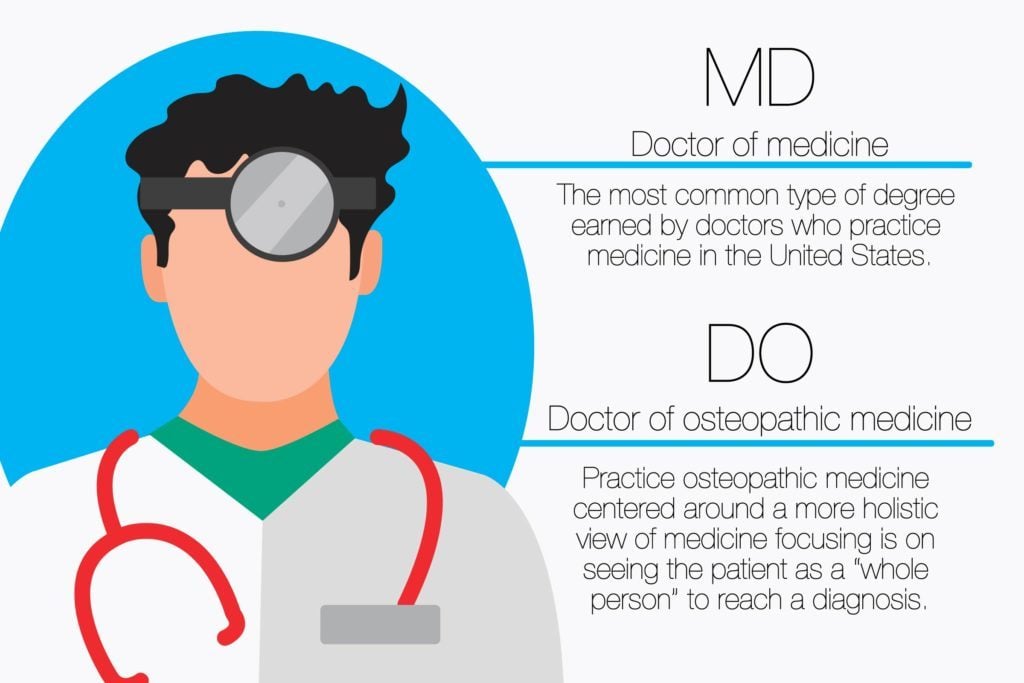
Wondering what's the difference between MD and DO? Let's delve into the distinctions between these medical professionals.
An MD (Doctor of Medicine) and a DO (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine) are both licensed physicians who provide comprehensive medical care. However, DOs receive additional training in osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM), a holistic approach that emphasizes the body's self-healing abilities and the importance of the musculoskeletal system.
This unique training allows DOs to offer a broader range of treatments, including manual adjustments, to address musculoskeletal conditions and promote overall well-being. Historically, the distinction between MDs and DOs arose from the development of osteopathy in the late 19th century.
What's the Difference Between MD and DO?
Distinguishing between MDs and DOs is crucial in understanding their roles and approaches to medical care. Here are eight key aspects that highlight their differences:
- Medical Training: MDs focus on conventional medicine, while DOs receive additional training in osteopathic manipulative medicine.
- Holistic Approach: DOs emphasize the body's self-healing abilities and consider the musculoskeletal system.
- Scope of Practice: DOs have similar practice rights to MDs but may use additional osteopathic techniques.
- Treatment Philosophy: MDs typically follow a more traditional medical approach, while DOs may incorporate OMM and other holistic therapies.
- Licensing and Accreditation: Both MDs and DOs are licensed physicians who must meet specific educational and training requirements.
- Historical Development: MDs originated from allopathic medicine, while DOs emerged from osteopathy in the late 19th century.
- Patient Demographics: DOs often have a broader patient base due to their holistic approach.
- Career Opportunities: MDs and DOs have similar career paths in various medical specialties.
These aspects underscore the unique strengths and perspectives of MDs and DOs, who both contribute to the comprehensive healthcare landscape.
Medical Training
In comparing MDs and DOs, their medical training stands out as a key differentiator. MDs primarily focus on conventional medicine, emphasizing pharmacological and surgical interventions. In contrast, DOs receive comprehensive training in osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM), a holistic approach that incorporates manual adjustments to address musculoskeletal issues and promote overall well-being.
- Conventional Medicine: MDs follow a traditional medical model, utilizing medications, surgeries, and other treatments to manage and cure diseases.
- Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine (OMM): DOs are trained in OMM, a hands-on technique that involves using gentle manipulations to improve the body's structure and function, often focusing on the musculoskeletal system.
- Holistic Approach: DOs emphasize the interconnectedness of the body's systems and focus on treating the whole person, not just the symptoms.
- Integrative Care: Many DOs combine conventional medicine with OMM, offering patients a more comprehensive and personalized approach to healthcare.
These distinctions in medical training shape the practice and philosophy of MDs and DOs, contributing to their unique roles in the healthcare system.
Holistic Approach
When comparing MDs and DOs, their holistic approach is a key differentiator. DOs emphasize the body's inherent ability to heal itself and place great importance on the musculoskeletal system's role in overall health.
- Whole-Person Care: DOs view the body as an integrated system and approach patient care by addressing physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
- Emphasis on Prevention: DOs focus on preventing illness and promoting health through lifestyle modifications, nutrition counseling, and stress management techniques.
- Patient-Centered Treatment: DOs actively listen to their patients and tailor treatment plans based on their individual needs and preferences.
- Integration of OMM: DOs use osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM) to address musculoskeletal issues and enhance the body's self-healing mechanisms.
This holistic approach sets DOs apart from MDs and allows them to provide comprehensive care that addresses not only the symptoms but also the root causes of illness. By considering the whole person and emphasizing the body's ability to heal, DOs aim to empower patients to take an active role in their own health and well-being.
Scope of Practice
In comparing MDs and DOs, it's important to consider their scope of practice, which encompasses the range of medical procedures and treatments they are licensed to perform. While MDs and DOs share similar practice rights, DOs are uniquely qualified to utilize osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM) as part of their patient care.
- Primary Care and Specialty Care: Both MDs and DOs can provide primary care services, such as check-ups, preventive care, and managing chronic conditions. They can also pursue specialty training in various fields such as cardiology, neurology, or orthopedics.
- Surgical Procedures: MDs and DOs are trained to perform a wide range of surgical procedures, from routine surgeries to complex operations. However, DOs may have additional training in osteopathic surgical techniques.
- Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine (OMM): DOs are licensed to use OMM, a hands-on approach that involves manipulating the musculoskeletal system to improve the body's structure and function. OMM can be used to address various conditions, including back pain, headaches, and sports injuries.
- Prescription Rights: Both MDs and DOs have the authority to prescribe medications as part of their patient care.
In summary, DOs have similar practice rights to MDs, allowing them to provide comprehensive medical care. However, their unique training in osteopathic manipulative medicine sets them apart, offering patients a more holistic and integrative approach to healthcare.
Treatment Philosophy
The difference in treatment philosophy between MDs and DOs stems from their distinct training and approach to patient care. MDs receive a more traditional medical education, emphasizing pharmacological and surgical interventions. DOs, on the other hand, are trained in osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM), a holistic approach that focuses on the body's self-healing abilities and the importance of the musculoskeletal system.
This difference in training leads to a different approach to patient care. MDs tend to follow a more conventional medical model, relying primarily on medications and surgeries to treat illnesses and injuries. DOs, on the other hand, may incorporate OMM into their treatment plans, using manual adjustments to improve the body's structure and function. They also emphasize preventive care and patient education, encouraging patients to take an active role in their own health.
The choice between an MD and a DO ultimately depends on the individual patient's preferences and needs. If you are looking for a physician who will provide comprehensive care that addresses both the physical and musculoskeletal aspects of your health, a DO may be a good option. However, if you prefer a more traditional medical approach, an MD may be a better fit.
Licensing and Accreditation
Licensing and accreditation are crucial components that define the differences between MDs and DOs. Both MDs and DOs must undergo rigorous educational and training programs to obtain their medical licenses, ensuring they possess the necessary knowledge and skills to provide competent medical care. These licensing and accreditation processes help maintain high standards within the medical profession, ensuring patient safety and trust.
The educational requirements for MDs and DOs are largely similar, typically involving pre-medical coursework, medical school, and residency training. However, DOs receive additional training in osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM), which sets them apart from MDs. OMM is a hands-on technique that involves using gentle manipulations to improve the body's structure and function, often focusing on the musculoskeletal system.
The practical significance of understanding the licensing and accreditation of MDs and DOs lies in making informed decisions about your healthcare providers. By knowing that both MDs and DOs are licensed physicians who have undergone rigorous training, you can feel confident in their ability to provide you with quality medical care. Additionally, if you are looking for a physician who incorporates OMM into their practice, you may want to consider a DO.
Historical Development
This historical distinction between MDs and DOs has significantly shaped the differences between their medical practices today. Allopathic medicine, which forms the foundation of MD training, focuses on treating specific symptoms and diseases using medications, surgeries, and other interventions. Osteopathy, on the other hand, emphasizes the body's inherent ability to heal itself and places great importance on the musculoskeletal system. DOs' training in osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM) allows them to address not only the symptoms but also the underlying causes of illness, promoting the body's natural healing processes.
The practical significance of understanding this historical development lies in recognizing the diverse approaches that MDs and DOs bring to patient care. While both are licensed physicians who provide comprehensive medical services, DOs' additional training in OMM gives them a unique skill set that can complement traditional medical treatments. This holistic approach can be particularly beneficial for conditions that involve musculoskeletal issues or chronic pain, as OMM can help improve the body's structure and function.
In conclusion, the historical development of MDs and DOs has played a critical role in shaping their distinct approaches to medical care. Understanding this history allows us to appreciate the complementary roles that these two professions play within the healthcare system and to make informed decisions about our healthcare providers.
Patient Demographics
In comparing MDs and DOs, patient demographics offer valuable insights into their practice differences. DOs' holistic approach and emphasis on the musculoskeletal system often attract a broader patient base in several ways:
- Preventive Care Seekers: DOs' focus on prevention and wellness resonates with patients seeking proactive healthcare to maintain optimal health.
- Musculoskeletal Conditions: Patients with musculoskeletal issues, such as back pain or sports injuries, often turn to DOs for their expertise in OMM and non-pharmacological pain management.
- Chronic Conditions: DOs' holistic approach can complement traditional treatments for chronic conditions, attracting patients seeking integrative care.
- Rural and Underserved Areas: In underserved areas where access to specialized healthcare is limited, DOs' broad scope of practice makes them valuable providers for diverse patient populations.
These factors contribute to DOs' broader patient base, demonstrating the value of their holistic approach in meeting the diverse healthcare needs of various patient demographics.
Career Opportunities
In comparing MDs and DOs, their career opportunities offer an important perspective. Both MDs and DOs can pursue diverse medical specialties, providing comprehensive healthcare services to patients.
- Specialization Options: MDs and DOs have access to a wide range of medical specialties, including internal medicine, pediatrics, surgery, psychiatry, and dermatology. This diversity allows them to pursue their interests and tailor their practice to specific areas of healthcare.
- Residency Training: To become specialists, both MDs and DOs must complete residency training programs accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME). These programs provide the necessary training and experience in their chosen specialty.
- Board Certification: After completing residency, MDs and DOs can obtain board certification from their respective specialty boards. Board certification demonstrates their expertise and commitment to continuing medical education.
- Practice Settings: MDs and DOs can work in various practice settings, including hospitals, clinics, private practices, and academic institutions. They may choose to focus on patient care, research, or a combination of both.
The similar career paths available to MDs and DOs highlight their shared commitment to providing high-quality medical care. By pursuing their interests and specializing in different areas of medicine, both MDs and DOs contribute to the diverse healthcare landscape and meet the diverse needs of patients.
In conclusion, our exploration of "what's the difference between MD and DO" has highlighted several key ideas:
- MDs and DOs share a commitment to providing comprehensive medical care but differ in their training and approach.
- DOs' holistic approach, incorporating osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM), complements traditional medical treatments.
- Both MDs and DOs have diverse career opportunities in various medical specialties.
Understanding these differences empowers patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare providers. As the medical landscape continues to evolve, the collaborative efforts of MDs and DOs are essential in meeting the diverse needs of patients and advancing the future of healthcare.
Andy Griffith: The Heartwarming Icon Of American Television
Unveiling Nik Makino's Net Worth: Strategies And Investments
The Ultimate Guide To Cameron Diaz: Wiki, Career, And Cultural Impact


ncG1vNJzZmifoqTCsbPKZ5imq2NjsaqzyK2YpaeTmq6vv8%2Bamp6rXpi8rnvWoZitq12ptaZ5w6Kdn52imruksYybnK2vlZq7brnDZpinnF2ZvG%2B006aj